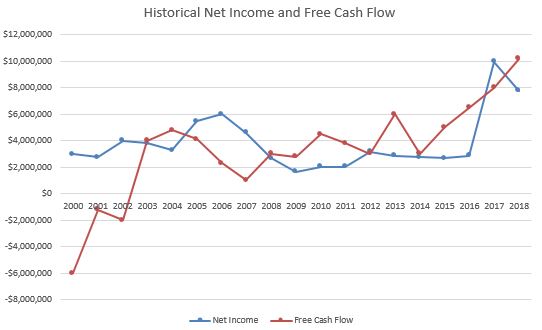
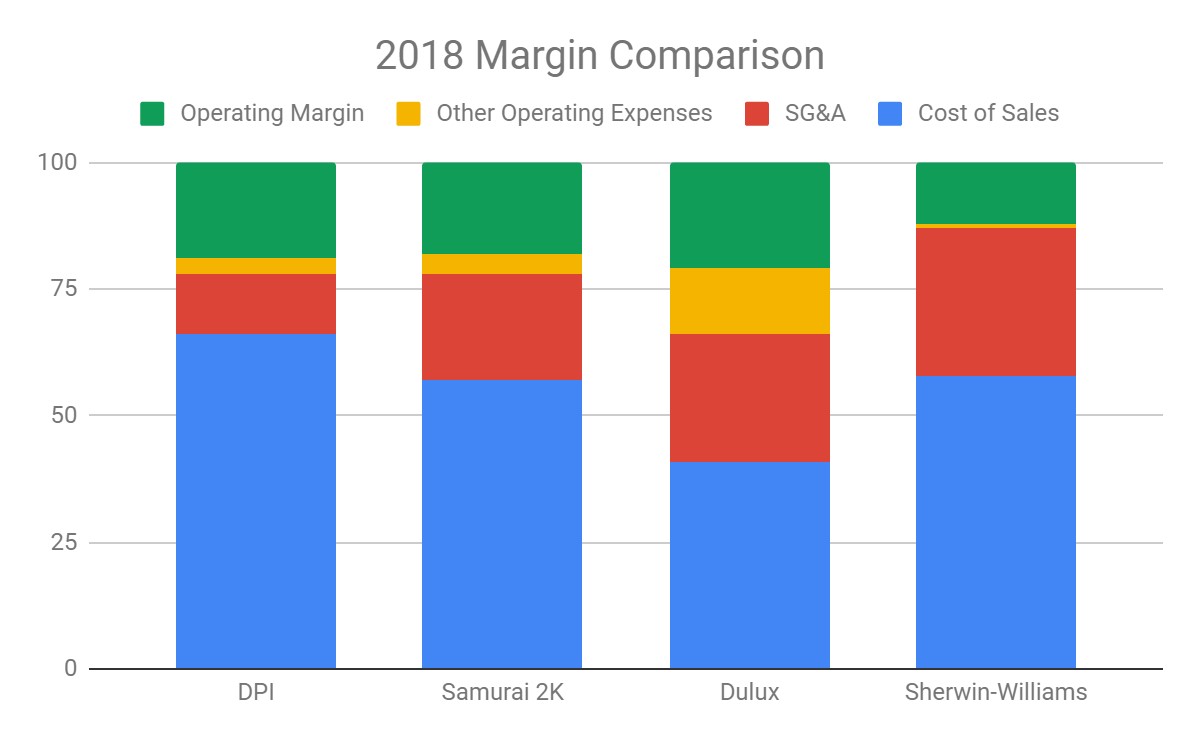
“Farmer Mac” A.K.A. Federal Agricultural Mortgage Corporation (AGM): The Freddie Mac of Farms and Ranches Has a P/E Below 9 and an ROE Above Most Banks
This is one of my “initial interest posts”. But, in this case it’s going to be more of an initial-initial interest post. I am in the early stages of learning about this company. And it’s likely to take me some time to get to the point where I can give as definitive a verdict on whether or not I’d follow up on the stock as I normally give in these posts.
First, let’s start with the obvious. As you probably guessed from the name, “Farmer Mac” is a government sponsored enterprise like Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae – except it operates in the agricultural instead of the residential market. The company has two main lines of business – again, this is just like the Freddie Mac business model except transplanted into the agricultural mortgage market – of 1) Buying agricultural (that is, farm and ranch) mortgages and 2) Guaranteeing agricultural (that is, farm and ranch) mortgages.
As a government sponsored enterprise operating in the secondary market for mortgages – the company has the two competitive advantages you’d expect. One, it has a lower cost of funds (on non-deposit money) because it issues debt that bond buyers treat as being ultimately akin to government debt. The same bond buyer might be willing to accept a 2.45% yield on a 10-Year U.S. Treasury bond and just a 3% yield on a Farmer Mac bond. This cost above the rate the U.S. government borrows at is much narrower for Farmer Mac than it is for most banks that make agricultural loans.
The other cost advantage is scale. Yes, there are banks – like Frost (CFR) – that have very low financial funding costs. But, these banks usually have to invest in hiring a lot of employees to build a lot of relationships, to provide customer service to retain customers, etc. that leads to a “total cost of funding” that is higher than what Farmer Mac has to pay. To put this in perspective, Frost’s deposits are basically the same as its earning assets (loans it makes plus bonds it buys). Frost has about $200 million in deposits per branch. This isn’t a bad number – it’s 1.5 times the deposits per branch of Wells Fargo and 2 times the deposits per branch of U.S. Bancorp (and more like 3-4 times the entire U.S. banking industry’s deposits per branch). Frost’s deposits per branch are pretty close to industry leading for a big bank. So, we can use that $200 million in deposits they have and assume a bank will almost never have more than $200 million in assets – because it doesn’t have more than $200 million in deposits – per branch. Farmer Mac has $200 million in assets per employee.
As a rule, one employee is going to cost you a lot less than one branch.
To put this in perspective, most banks spend more on rent relative to their assets than Farmer Mac spends on everything relative to its assets.…
Read more
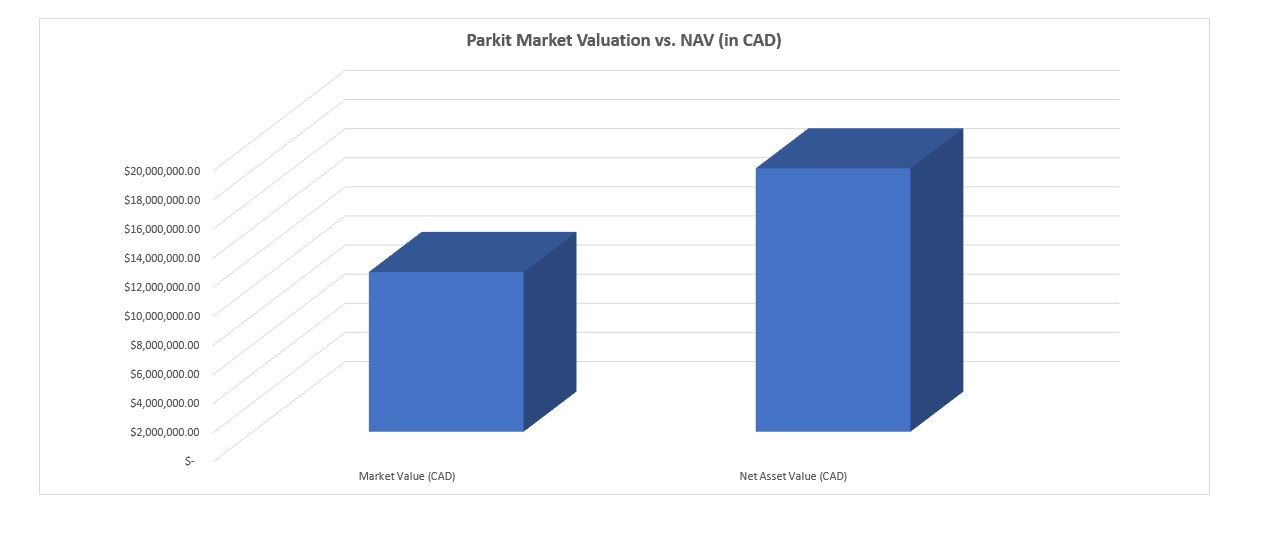 (Image Created by the Author; Data via Parkit Investor Relations Page and Author’s Calculations)
(Image Created by the Author; Data via Parkit Investor Relations Page and Author’s Calculations)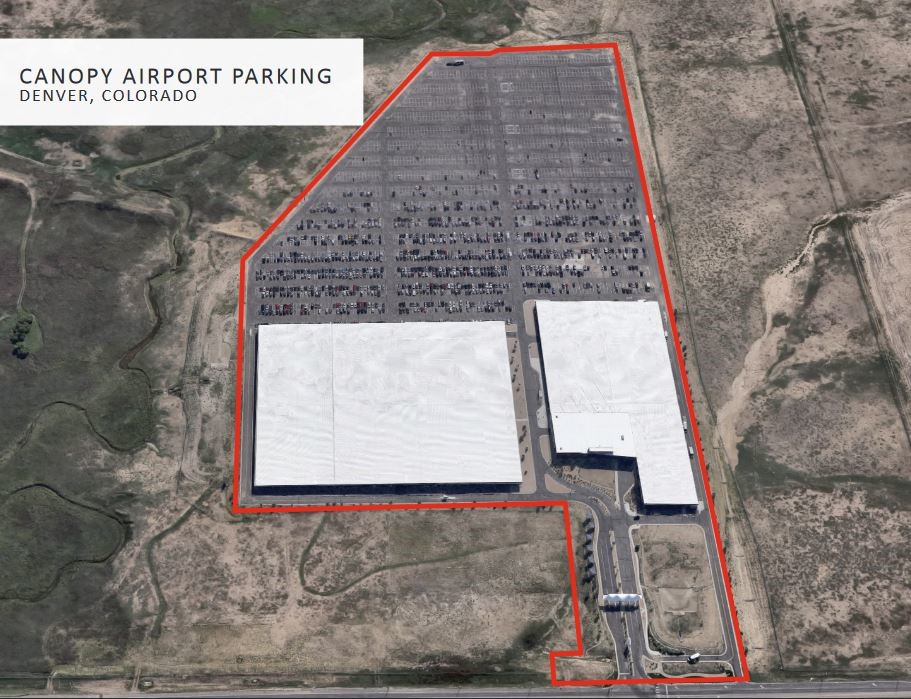 (Source: Parkit Investor Presentation, April …
(Source: Parkit Investor Presentation, April …